Trichomonas vaginalis - Introduction, History, Habitat, Morphology, Culture
Introduction of Trichomonas vaginalis
Trichomonas vaginalis is the simplest of all protozoan parasites as it has only one morphological form- the trophozoite form. Other important properties of the parasite include an anterior tuft of flagella, an undulating membrane with recurrent flagella, and an axostyle.
Trichomonas vaginalis causes sexually transmitted infection of the genital tract in humans, commonly in women than men, called trichomoniasis.
They are anaerobic obligate parasites that ferment sugars in a structure called hydrogenosomes to produce energy. The hydrogenosome is modified mitochondria.
History of Trichomonas vaginalis
Historically, in 1837, the flagellate was first observed by Donne.
Habitat of Trichomonas vaginalis
Trichomonas vaginalis inhabits the vagina of the infected female and in the prostate, seminal vesicles in the infected male. In both sexes, the parasite is also present in the urethra.
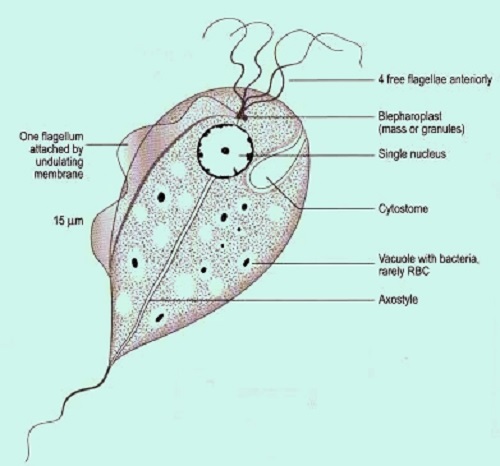
Fig: T. vaginalis morphology (Source: Labweeks)
Morphology of Trichomonas vaginalis
only one morphological stage of Trichomonas vaginalis
measures 7μm – 23 μm in length
motility is achieved by the presence of 5 flagella and is described as a “twitching” type of motility
the four anterior flagella arise from the shallow depression while the fifth flagellum (called recurrent flagellum) curves back along the margin of the undulating membrane
the shallow depression in the anterior end of the body is called the paraflagellar canal
Costa, which is a rigid filamentous cord unique in trichomonads, lies beneath the membrane and functions by supporting the undulating membrane
the hyaline rod structure called axostyle is a part of the exoskeleton that runs through the entire length of the body and comes out at the posterior end
Trichomonas vaginalis cytoplasm contains siderophil granules in large numbers and may also contain viral particles
Image: T. vaginalis microscopy (Source: YouTube)
Culture of Trichomonas vaginalis
for routine tests, Trichomonas vaginalis can be cultured in in-vitro in culture media such as Diamond, Lash, and Kupferberge medium.
These mediums contain yeast extract, horse medium, and antibiotics. The parasite is incubated for seven days
for research purposes, Simplified trypticase serum (STS) medium is used for bacteria-free axenic culture
in animals, Trichomonas vaginalis can be cultured in mice and guinea pigs