Insect respiratory system
•Download as PPTX, PDF•
2 likes•4,296 views
This document summarizes the respiratory system of insects. It describes how insects obtain oxygen and release carbon dioxide through a system of internal air-filled tubes called tracheae that branch throughout the body and connect to external openings called spiracles. The document outlines the different types of respiratory organs in insects including spiracles, tracheae, and air sacs. It also describes the mechanisms of gas exchange and different types of respiration in aquatic versus terrestrial insects.
Report
Share
Report
Share
Recommended
Recommended
More Related Content
What's hot
What's hot (20)
structure and function of insect respiratory system

structure and function of insect respiratory system
Similar to Insect respiratory system
Similar to Insect respiratory system (20)
Comparative Anatomy of Respiratory System of Vertebrates

Comparative Anatomy of Respiratory System of Vertebrates
Modification in respiratory organs and respiration in endoparasitic insects

Modification in respiratory organs and respiration in endoparasitic insects
Presentation on Organ & Mechanism of Respiration in Pisces And Amphibians

Presentation on Organ & Mechanism of Respiration in Pisces And Amphibians
More from Karunya Institute of technology and sciences
More from Karunya Institute of technology and sciences (15)
Recently uploaded
Antibiotics are medicines that fight infections caused by bacteria in humans and animals by either killing the bacteria or making it difficult for the bacteria to grow and multiply. Bacteria are germsABHISHEK ANTIBIOTICS PPT MICROBIOLOGY // USES OF ANTIOBIOTICS TYPES OF ANTIB...

ABHISHEK ANTIBIOTICS PPT MICROBIOLOGY // USES OF ANTIOBIOTICS TYPES OF ANTIB...ABHISHEK SONI NIMT INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL AND PARAMEDCIAL SCIENCES , GOVT PG COLLEGE NOIDA
In recent years, the growth of scientific data and the increasing need for data sharing and collaboration in the field of environmental chemistry has led to the creation of various software and databases that facilitate research and development into the safety and toxicity of chemicals. The US-EPA Center for Computational Toxicology and Exposure has been developing software and databases that serve the chemistry community for many years. This presentation will focus on several web-based software applications which have been developed at the USEPA and made available to the community. While the primary software application from the Center is the CompTox Chemicals Dashboard almost a dozen proof-of-concept applications have been built serving various capabilities. The publicly accessible Cheminformatics Modules (https://www.epa.gov/chemicalresearch/cheminformatics) provides access to six individual modules to allow for hazard comparison for sets of chemicals, structure-substructure-similarity searching, structure alerts and batch QSAR prediction of both physicochemical and toxicity endpoints. A number of other applications in development include a chemical transformations database (ChET) and a database of analytical methods and open mass spectral data (AMOS). Each of these depends on the underlying DSSTox chemicals database, a rich source of chemistry data for over 1.2 million chemical substances. I will provide an overview of all tools in development and the integrated nature of the applications based on the underlying chemistry data. This abstract does not necessarily represent the views or policies of the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency.Chemistry Data Delivery from the US-EPA Center for Computational Toxicology a...

Chemistry Data Delivery from the US-EPA Center for Computational Toxicology a...US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), Center for Computational Toxicology and Exposure
Recently uploaded (20)
COMPOSTING : types of compost, merits and demerits

COMPOSTING : types of compost, merits and demerits
TransientOffsetin14CAftertheCarringtonEventRecordedbyPolarTreeRings

TransientOffsetin14CAftertheCarringtonEventRecordedbyPolarTreeRings
Porella : features, morphology, anatomy, reproduction etc.

Porella : features, morphology, anatomy, reproduction etc.
Efficient spin-up of Earth System Models usingsequence acceleration

Efficient spin-up of Earth System Models usingsequence acceleration
Selaginella: features, morphology ,anatomy and reproduction.

Selaginella: features, morphology ,anatomy and reproduction.
Cyathodium bryophyte: morphology, anatomy, reproduction etc.

Cyathodium bryophyte: morphology, anatomy, reproduction etc.
ABHISHEK ANTIBIOTICS PPT MICROBIOLOGY // USES OF ANTIOBIOTICS TYPES OF ANTIB...

ABHISHEK ANTIBIOTICS PPT MICROBIOLOGY // USES OF ANTIOBIOTICS TYPES OF ANTIB...
Understanding Partial Differential Equations: Types and Solution Methods

Understanding Partial Differential Equations: Types and Solution Methods
Information science research with large language models: between science and ...

Information science research with large language models: between science and ...
Genome Projects : Human, Rice,Wheat,E coli and Arabidopsis.

Genome Projects : Human, Rice,Wheat,E coli and Arabidopsis.
Fourth quarter science 9-Kinetic-and-Potential-Energy.pptx

Fourth quarter science 9-Kinetic-and-Potential-Energy.pptx
POGONATUM : morphology, anatomy, reproduction etc.

POGONATUM : morphology, anatomy, reproduction etc.
X-rays from a Central “Exhaust Vent” of the Galactic Center Chimney

X-rays from a Central “Exhaust Vent” of the Galactic Center Chimney
The Mariana Trench remarkable geological features on Earth.pptx

The Mariana Trench remarkable geological features on Earth.pptx
SaffronCrocusGenomicsThessalonikiOnlineMay2024TalkOnline.pptx

SaffronCrocusGenomicsThessalonikiOnlineMay2024TalkOnline.pptx
Chemistry Data Delivery from the US-EPA Center for Computational Toxicology a...

Chemistry Data Delivery from the US-EPA Center for Computational Toxicology a...
Insect respiratory system
- 1. Prepared by Dr. S. Sumaiya
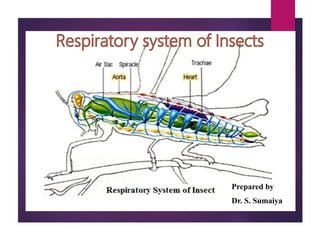
- 2. Respiratory system Similar to aerobic animals, insects must obtain oxygen from their environment and eliminate carbon dioxide respired by their cells. Gas exchange occurs by means of internal air-filled tracheae. These tubes branch and ramify through the body. The finest branches called tracheole contact all internal organs and tissues and are numerous in tissues with high oxygen requirements. Air usually enters the tracheae via spiracular openings positioned laterally on the body. No insect has more than ten pairs (two thoracic and eight abdominal).
- 3. Based on the number and location of functional spiracles respiratory system is classified as follows
- 4. Organs of respiration Spiracles Spiracles have a chamber or atrium with a opening and closing mechanism called valve. This regulates air passage and minimize water loss. Each spiracle is set in a sclerotized cuticular plate called a peritreme. 1. Simple type 2. Atriate type: Lip type & Valve type
- 5. Tracheae Large tubes of tracheal system Communicates with external environment by means of small opening – Spiracles Divides into smaller braches - Tracheoles The ringed appearance of the tracheae is due to the spiral ridges called taenidia. Cuticular lining – Intima – shed along old cuticle during molting
- 6. Air sacs In the trachea, thin walled-collapsable sac like dilations are present, called as airsacs where taenidia is absent. Airsacs acts as oxygen reservoir. Provide buoyancy to flying and aquatic insects. Provide space for growing organs. Acts as sound resonator and heat insulators.
- 7. Mechanism of respiration Oxygen enters the spiracle and passes through the length of the tracheae to the tracheoles and into the target cells by a combination of ventilation and diffusion along a concentration gradient, from high in the external air to low in the tissue. Where as the net movement of oxygen molecules in the tracheal system is inwards (Inspiration), the net movement of CO 2 and water vapour molecules is outwards, (Expiration).
- 8. Types of Respiration Respiration in aquatic insects 1. Closed tracheal system In some aquatic and many endoparasitic larvae spiracles are absent and the tracheae divide peripherally to form a network. This covers the body surface, allowing cutaneous gas exchange. e.g. Gills : Tracheated thin outgrowth of body wall. Lamellate gills - mayfly naiad Filamentous gills - damselfly naiad Rectal gills - dragonfly naiad
- 9. Open tracheal system i. Air store: Air bubble stored beneath wings acts as physical gill, e.g. water bug. ii. Respiratory siphon - e.g. Wriggler iii. Caudal breathing tube -e.g. Water scorpion iv. Plastron: Closely set hydrofuge hairs of epicuticle hold a thin film of air indefinitely. E.g. Water beetles Types of Respiration