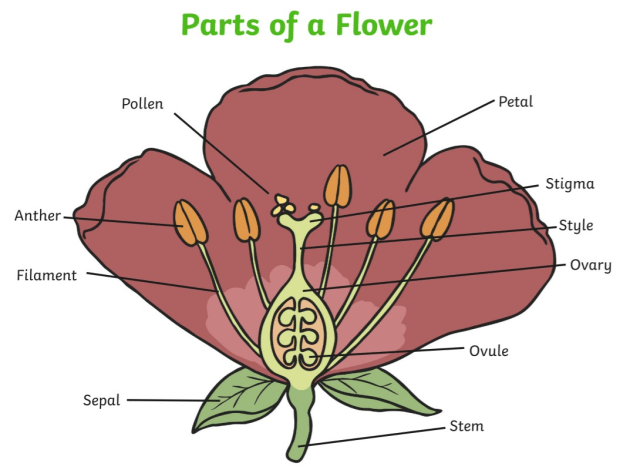
The anther is the part of the stamen in a flower where pollen is produced.
Pollen is the fine powdery substance produced by flowering plants that contains the male gamete of the flower. It attracts pollinators like bees and other insects to the plant. They carry pollen between plants which starts the process of seeds developing. This is an integral part of the process of reproduction in plants.
You can see the anthers by looking at the parts which stick out from the middle of the flower and have pollen on them. The anthers are the oval structure on the end of the filament of the stamen. They can be different colours but most anthers are yellow, orange, or red. Most flowers have around five anthers, but different types of flowers have different amounts.
The anthers are important because they help the flower to create pollen. Without the anthers of the flower producing pollen, the flower cannot reproduce.
The filaments of the stamen hold the anthers up and away from the main body of the flower. This is so that passing pollinators, like bees, can brush against the anther. This means that pollen transfers onto the pollinator, which is covered in tiny hairs. As they travel between plants, the pollinator transfers pollen from one to the next. When the bee buzzes along to another flower, the pollen falls onto the female organs of the flower.

Now that you know about what the anther of a flower looks like and what it does, it is time to learn about the other parts of a flower.
You can find out more about the parts of a plant with our informative Teaching Wiki. This includes information for KS2 pupils about the characteristics of a plant, as well as its flowers, leaves, stems, and roots.
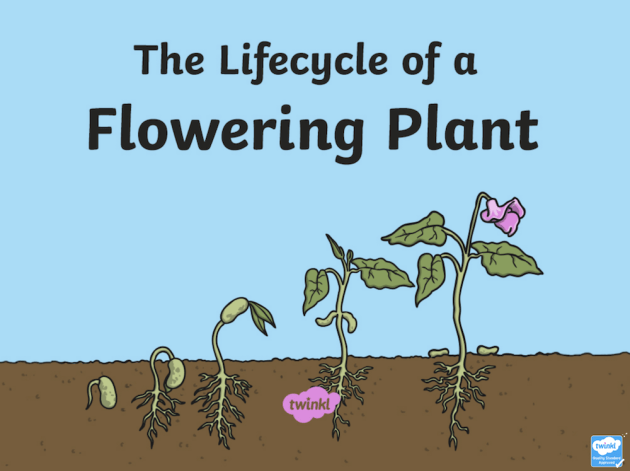
Plants can reproduce in two ways: sexually or asexually. Asexual reproduction only requires one plant to make more plants. Some plants that reproduce asexually are daffodils. Sexual reproduction requires male and female gametes to make a new plant.
To reproduce, male gametes in pollen need to meet the female gametes in the ovules. This process is called pollination. A pollen grain has to land on the stigma of a flower – but the flower has to be the same species. Once the pollen grain has landed on the stigma, it grows a tube down into the ovary to find an ovule. This process is called fertilisation.
After fertilisation occurs, seeds are dispersed, and a new plant grows. This is the beginning of the plant’s life cycle.
We hope you have learnt a bit more about the anther and its role within the plant! You can find many more resources on our website to help you to teach and learn about plants and their life cycles. We’ve chosen a few of our favourite resources to get you started.
 Home
Home  Membership
Membership  Customer Support
Customer Support  Create
Create  Blog
Blog